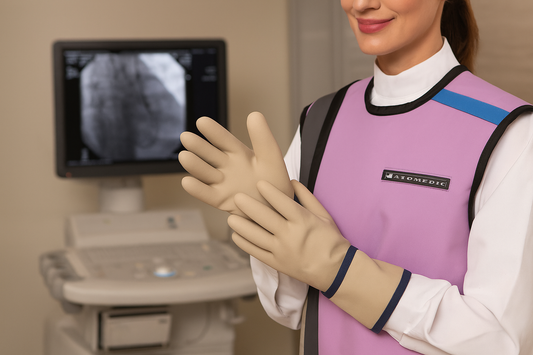
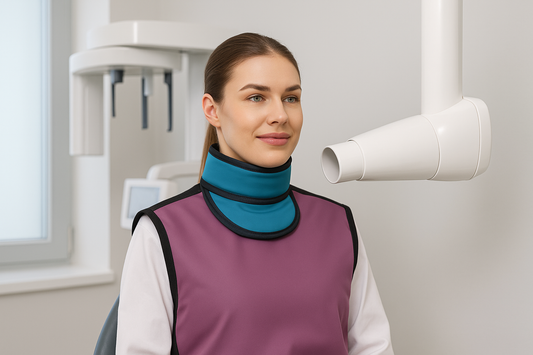
Radiation protection is a non-negotiable part of working in healthcare environments where diagnostic imaging, fluoroscopy, and interventional procedures are performed. From hospitals to dental practices, staff safety is as important as patient care. Among the most essential pieces of protective equipment is the radiation protection vest.
Unlike traditional aprons, vests are designed to shield vital organs while distributing weight more ergonomically across the shoulders and torso. For professionals who spend long hours standing and assisting with procedures, this difference can mean the prevention of back pain, improved mobility, and greater long-term health outcomes.
But not all radiation protection vests are created equal. Choosing the right one requires an understanding of safety standards, fit, comfort, materials, and certification.
Benefits of Radiation Protection Vests
Targeted Shielding for Vital Organs
Radiation vests are designed to protect the chest, abdomen, and back from harmful scatter radiation. By safeguarding critical organs—including the heart, lungs, and reproductive organs—they provide peace of mind during procedures that rely heavily on X-rays.
Ergonomic Design to Reduce Strain
Traditional aprons can place significant strain on the lower back and shoulders. Radiation protection vests, especially those designed with ergonomic cuts and adjustable straps, distribute weight more evenly. This makes them the preferred option for staff who wear protection for extended periods.
Durability for Everyday Demands
Radiology and surgical environments are fast-paced. Protective gear must endure frequent wear, handling, and cleaning. Quality vests are built with reinforced seams, tough outer fabrics, and reliable shielding cores that withstand the test of time.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Vest
1. Certification and Standards
Safety should never be assumed. Radiation protection vests must meet regulatory standards, such as IEC or ASTM guidelines, and demonstrate proper lead equivalence for shielding effectiveness. Certification provides assurance that the product has been rigorously tested and approved for clinical use.
2. Fit and Size
A poorly fitted vest compromises safety. Too loose, and gaps may expose the wearer to scatter; too tight, and it may restrict movement. Vests should be available in multiple sizes, with adjustable closures and panels to ensure a snug yet comfortable fit. Proper fit testing before purchase is recommended.
3. Comfort and Ergonomics
Healthcare professionals often wear vests for hours at a time. Comfort features such as padded shoulders, breathable fabrics, and contoured cuts prevent fatigue. An ergonomic vest improves posture, reduces strain on the spine, and ensures professionals can focus on patients—not discomfort.
4. Lead vs Lead-Free Materials
Both options provide effective shielding, but each comes with advantages:
-
Lead Vests: Proven, cost-effective, and widely available.
-
Lead-Free Vests: Lighter, eco-friendly, and safer to dispose of at the end of life.
The choice often depends on personal preference, budget, and institutional sustainability policies.
5. Thickness and Level of Protection
Vests are available in different millimetres of lead equivalence (e.g., 0.25mm, 0.35mm, 0.5mm). The right thickness depends on the procedure type and level of exposure. Higher equivalence offers greater protection but adds weight. A balance between safety and wearability is key.
6. Longevity and Maintenance
A vest should provide years of service if properly cared for. Look for reinforced stitching, durable outer shells, and flexible cores that resist cracking. Ease of cleaning is also vital—outer materials should withstand hospital-grade disinfectants without degrading.
7. Mobility and Design Options
Some professionals prefer two-piece sets (a vest paired with a skirt) for improved mobility and reduced strain on the hips. Wraparound styles offer extra protection by covering the sides of the body. Consider the type of procedures performed most often when choosing a design.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are vests better than aprons?
For professionals who experience back strain or wear protection for long hours, vests are generally more ergonomic. Aprons remain a good option for quick procedures, but vests are better suited to extended use.
Do vests come in different thicknesses?
Yes. Most vests range from 0.25mm to 0.5mm lead equivalence. The choice depends on the level of radiation exposure expected during procedures.
Are they comfortable to wear all day?
Modern designs prioritise comfort with padded shoulders, breathable linings, and ergonomic tailoring. Choosing the right fit is essential for all-day comfort.
Do all vests offer certification?
Not necessarily. Always verify that the vest complies with international radiation protection standards before purchase.
How long do radiation vests last?
With proper care, a high-quality vest can last several years. Annual inspections are recommended to check for cracks or wear in the shielding material.
What’s the difference between lead and lead-free vests?
Lead vests are heavier but cost-effective. Lead-free vests use composite materials, making them lighter and environmentally responsible. Both protect effectively when certified.
Can radiation vests be cleaned easily?
Yes, but harsh chemicals should be avoided. Use approved disinfectants, and always follow manufacturer instructions to prevent damage.
Helping Professionals Choose Wisely
Radiation protection vests are more than just workwear—they are investments in long-term health and professional performance. Choosing the right vest means balancing safety certifications, comfort, durability, and practicality.
For healthcare professionals who want trusted protection, the CavoMed Radiation Protection Vests combine proven safety standards with ergonomic design and lasting durability. Built for daily use, these vests ensure staff remain safe, supported, and comfortable throughout their practice.